4 - Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Disposable items of PPE you might require at the point of care delivery. • gloves• aprons• gown• masks• eye/face protection
Deciding which PPE to use
Before doing any procedure or task staff should risk assess any likely exposure to blood and/or body fluids and ensure PPE is worn that provides adequate protection against the risks associated with the procedure or task being undertaken.
All PPE should be:
- located close to the point of use
- stored in a clean and dry area to prevent contamination until needed for use
- within expiry dates
- single-use only items unless specified by the manufacturer
- changed immediately after individual use and/or following completion of a procedure or task
- disposed of after use into the correct waste stream as per local risk assessed processes
Reusable PPE items, for example non-disposable goggles, face shields or visors must be cleaned/decontaminated once removed or placed within a designated container for subsequent cleaning/decontamination with decontamination schedules in place and responsibility assigned.
Gowns, headwear and footwear are unlikely to be required within a care home setting. Please refer to the NIPCM for guidance on use.

Read further information on best practice for PPE in Appendix 15.
Donning (putting on) personal protective equipment (PPE)
The order for putting on PPE is:
- apron or gown
- surgical mask
- eye/face protection (where required)
- gloves
Doffing (taking off) personal protective equipment (PPE)
It is important that PPE is removed in the correct order.
The order for taking off PPE is:
- gloves
- apron or gown
- eye/face protection (if worn)
- surgical mask
Note:
Always carry out hand hygiene immediately after taking off PPE.
If using eye and face protection hand hygiene should be carried out after removing the apron or gown and before removing eye and face protection.
All PPE should be removed removed, followed by hand hygiene, before leaving the area and disposed of as healthcare waste.
Resources
 A poster showing the order for putting on and removing PPE is available to print.
A poster showing the order for putting on and removing PPE is available to print.
Select image for full size version
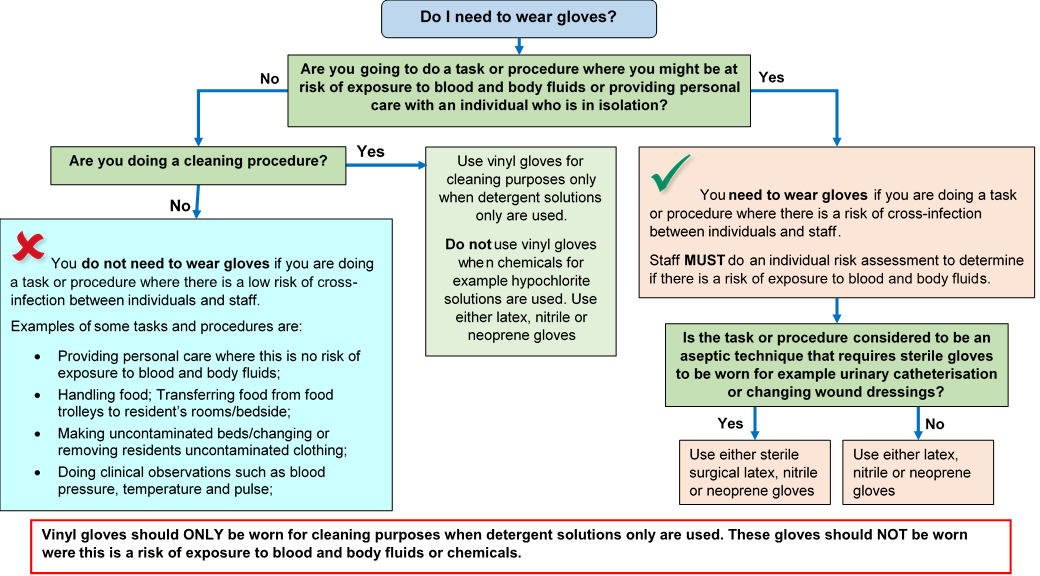
Gloves
Gloves should be:
- worn when it is likely or anticipated that you will be exposed to blood, body fluids (including but not limited to secretions and/or excretions), non-intact skin, mucous membranes, lesions and/or vesicles, hazardous drugs, and chemicals for example cleaning agents
- single-use and should be donned (put on) immediately prior to exposure risk and should be doffed (taken off) immediately after each use or upon completion of a task
- appropriate for use, fit for purpose and well-fitting. The glove selection chart can help you select the correct gloves
- changed if damaged or a perforation or puncture is suspected
Note:
Using gloves reduces the risk of contamination but does not remove all risk.
Gloves should not be used instead of carrying out hand hygiene.
Gloves should not be worn inappropriately in situations such as to go between residents, move around a care area or whilst at workstations (on the telephone or computer).
Gloves should never be decontaminated or cleaned with hand rub or by washing with cleaning products.
![]() Use the glove selection chart to support you to select the correct glove type.
Use the glove selection chart to support you to select the correct glove type.
Select image for full size version
Aprons and gowns
Selection of aprons or gowns for use in health and care settings should be based on an assessment of the task to be undertaken, and the anticipated levels of blood or body fluid exposure.
Aprons should be:
- disposable
- fluid repellent
- used to protect the uniform, workwear or clothes to prevent exposure or contact with another person’s:
- blood or bodily fluids (including urine, faeces, vomit, nasal discharge, wounds, sores)
- mucous membranes (including nose and mouth)
- rashes (confirmed or suspected scabies)
- leaking vesicles (confirmed or suspected shingles)
- used to protect uniform, workwear or clothes when exposure or contact with hazardous drugs, chemical or cleaning products is likely
- used to protect uniform, workwear or clothes when contact or exposure or handling of used, soiled, or infectious linen /laundry is likely
- to protect uniform, workwear or clothes when providing direct care to a resident during assisted toileting, or eating
- regarded as single use items which should never be reused (one resident, one task, one apron)
Eye/face protection
Eye/face protection should:
- be worn when there is an anticipated risk of splashing or spraying of blood or bodily fluids and always during Aerosol Generating Procedures (AGPs)
Note:
Eye/face protection should not be touched when worn or worn around the neck or on top of the head when not in use.
Eye/face protection should be compatible with other items of PPE and worn in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions.
Prescription eyeglasses and contact lenses should not be considered a form of eye/face protection.
Fluid Resistant Type IIR surgical face masks (FRSM)
Fluid Resistant Type IIR surgical face masks should be:
- worn if splashing or spraying of blood, body fluids, secretions or excretions onto the respiratory mucosa (nose and mouth) is expected/likely. (As part of SICPs a full-face visor may be used as an alternative to fluid resistant Type IIR surgical face masks to protect against splash or spray)
- well-fitting, fully covering the mouth and nose and fit for purpose. Manufacturer’s instructions should be followed to ensure effective fit/protection
- removed or changed:
- at the end of a procedure/task
- if the mask is damaged or there is a build up from moisture after prolonged use or from gross contamination with blood or body fluids
- following specific manufacturers’ instructions
If you are using droplet precautions, you should always wear a Type IIR surgical face mask as well as eye/face protection (droplet precautions will be discussed further in Chapter 2 Transmission Based Precautions).
Transparent face masks
Transparent face masks may be used to aid communication with residents where required.
Transparent face masks should:
- meet the specification standards of the Transparent face mask technical specification
and
- have been approved for use within health and social care settings
- only be worn in areas where Fluid Resistant Type IIR surgical face masks are used as personal protective equipment
Resources
 Read the aerosol generating procedures literature review and surgical face masks literature review for further information regarding the evidence base.
Read the aerosol generating procedures literature review and surgical face masks literature review for further information regarding the evidence base.
See appendix 11 for further information.
PPE for visitors
Where visitors are undertaking any direct care activities which may result in them encountering blood or other bodily fluids, they should also be offered the opportunity to use items of PPE (PPE for visitors link to be added) to protect them from infectious agents.
A decline by any visitor should be respected, following an explanation of potential risks, and the visit allowed to maintain the resident’s ability to spend time with those important to them.
Advice on the correct use of PPE should be provided, but its use by visitors cannot be enforced.
Table 1: PPE use for care home visitors
| PPE Item to offer | Gloves | Aprons | Face mask | Goggles, visors, face shields for eye/face protection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| When to use PPE | If providing direct care which exposes them to blood and/or body fluids for example assisted toileting or feeding. | To protect clothing if they intend to provide direct care which will expose them to someone’s blood/ or bodily fluids, or there is likely to be splashing of blood or bodily fluids during care delivery | To protect their nose and mouth from likely splash/spray of someone’s blood or bodily fluids or if they are entering the room of a resident with any suspected or known respiratory infection | To protect their face and eyes from any likely splash or spray from someone’s blood or bodily fluids |
 Read the PPE literature reviews to find out more information about the evidence base for PPE use.
Read the PPE literature reviews to find out more information about the evidence base for PPE use.